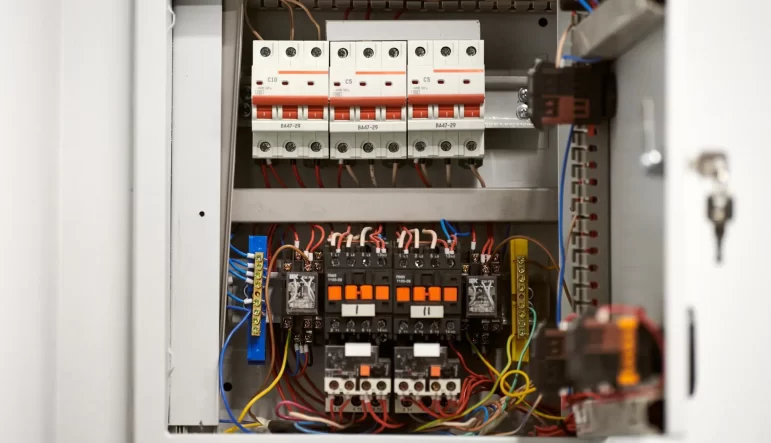
Electrical distribution boxes are used in commercial and residential buildings and are part of the electrical system, also known as switchboards. It integrates power distribution, protection, and monitoring capabilities, and is responsible for distributing power to entire commercial or residential buildings. To put it bluntly, the distribution box is the control and distribution center of electricity.
Distribution boxes vary in shape and structure due to different usage scenarios and requirements, but the basic components include fuses, circuit breakers, SPDs, switches, bypass devices, various insulating materials, wires, bus bars, and other components.
In order to ensure the electrical safety of the building, the distribution box needs to have strict quality control, and must ensure function and use:
According to different usage scenarios and requirements, there are several types of distribution boxes:
The main and most common distribution panel. Electricity travels through the wires first to a meter that records usage and then to a circuit breaker panel. The circuit breaker panel plays the role of protecting and monitoring the circuit during use. In the case of circuit overheating and short circuit faults, the components in the circuit breaker panel can detect the fault and cut off the circuit to prevent subsequent greater damage.
The main lug panel is basically located downstream of the main circuit breaker panel and is a sub-panel used to increase the number of circuits. In the main lug panel, the upstream input wires are connected directly to the lugs. In use, it can share the load of the main circuit breaker panel to meet the increasing power demand.
The relatively small size of the sub-panel allows for more detailed power distribution to specific areas or rooms. From the internal components, there is the position of the circuit breaker. In this way, specific areas or rooms can be protected during use.
For places with special power requirements, in order not to affect the power consumption of other areas, it is more convenient to install and use a sub-panel. Such as garages, office rooms, etc.
The fuse box uses disposable fuses to protect the circuit from damage caused by overloads and short circuits. Inside a fuse is a thin, fusible strip of metal called the fuse element. When the current passing through it reaches a certain value, it will heat up and melt to cut off the circuit.
Fuses have a much faster reaction time than circuit breakers and are suitable for protecting sensitive electronic equipment.
The transfer switch can switch the load between the two power supplies. It is an electrical switch. When the main power supply fails or fails, the main power supply can be switched to the backup power supply through the transfer switch. On the market, there are manual transfer switches and automatic transfer switches. In comparison, the manual transfer switch is cheaper and easier to install, while the automatic transfer switch can automatically switch the power supply in time. For places with demand, automatic transfer switches are essential, such as hospitals and so on.
Transfer switches are used in various scenarios. According to different needs, there are many specifications for transfer switches to choose from.
The distribution box is an indispensable part of the electrical system. Only when the shell quality meets the requirements can it be used safely and securely. The material of the distribution box shell should meet the following requirements:
Due to different usage scenarios and requirements, as well as considering the location of the actual wiring, the distribution box has a variety of sizes, which can be selected on the distribution box page.
You can see how many circuits are on the periphery of the box to divide the circuit. 8 circuits and below will basically be used for home use, and more than 8 circuits will basically be used for commercial and factory power distribution. The greater the demand for circuit branches, the larger the distribution box can be selected to meet the demand.
Distribution boxes are very important. It integrates wires, so there is no need to connect each device to the power supply separately, which saves the length of wires, simplifies the circuit structure, and ensures the efficiency of use. It can also ensure the safety of building electrical electricity.
In the distribution box, commonly known as the distribution board or breaker panel, you’ll find several critical components responsible for managing and distributing electrical power throughout a building or home. These components typically include:
Circuit Breakers:The primary safety device that prevents electrical overloads and short circuits.It has basic circuit protection functions, including overload protection, over-under-voltage protection, and so on.
Installation of a distribution box is a critical task that should ideally be performed by a qualified electrician. However, providing a step-by-step guide can be informative for those interested in the process. It may include:
When purchasing a new circuit breaker distribution box, several criteria should be considered:
| M | T | W | T | F | S | S |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | ||||||
| 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 |
| 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 |
| 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 | 22 |
| 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 | |

tongou was established in 1993 and is the trademark of Changyou Technology. We position ourselves as providers of intelligent product solutions for high and low voltage electrical systems, taking on solving customers’ pressures and challenges as our responsibility and creating value for them. We utilize intelligent products to serve global customers, making life smarter and more convenient to benefit your life.
Paidong Industrial Zone Qiligang,Yueqing City,Zhejiang province,China.
Sales: [email protected]
After-sales: [email protected]
© 2025 Changyou Technology. All Rights Reserved.